Author(s): Chuqin Huang a, Yanda Cheng a, Xiaoyu Zhang b, Ye Zhan c, Wenhan Zheng a, Isabel Komornicki d, Linda M. Harris d, Wenyao Xu b, Jun Xia a
ABSTRACT
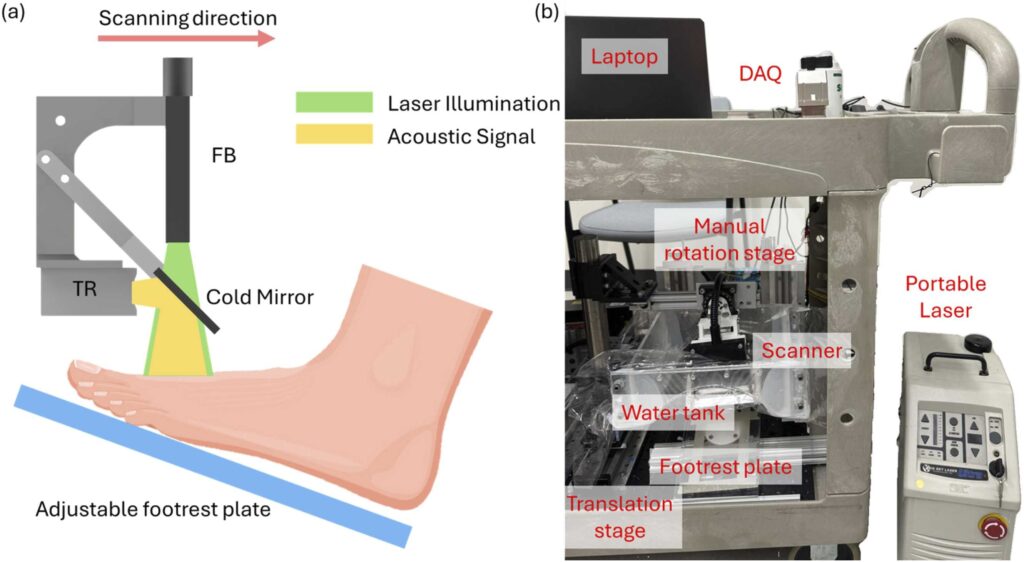
Accurate assessment of tissue perfusion is essential for managing chronic foot ulcers in patients with diabetes and peripheral arterial disease. While photoacoustic (PA) imaging enables high-resolution visualization of vascular structures, current perfusion evaluation methods are limited. We propose a fully automated radiomics-based framework for predicting perfusion conditions using single-wavelength clinical PA foot imaging. Radiomics features were extracted from both raw radiofrequency (RF) signals and reconstructed maximum amplitude projection (MAP) images. After reproducibility testing and statistical filtering, features were ranked using a combined minimum redundancy maximum relevance (mRMR) and ReliefF approach. A k-nearest neighbors ensemble model trained on eight selected features achieved an area under the curve (AUC) of 0.90 (training) and 0.94 (test). The selected features corresponded with physiological indicators such as vessel density, tissue structure, and vascular discontinuity. This study demonstrates a reliable and interpretable method for perfusion assessment in PA imaging with strong clinical potential.
